- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
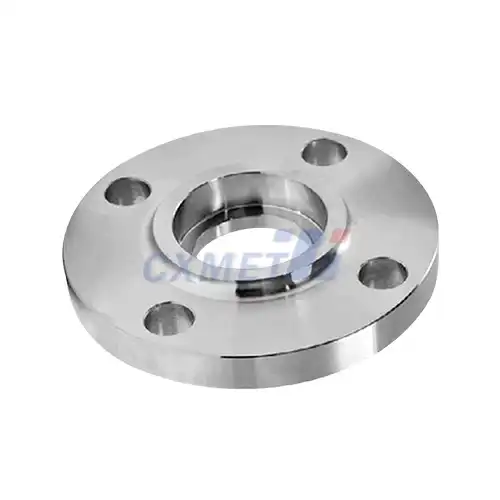
What are the Different Sizes and Specifications for Titanium Blind Flanges?
2024-10-10 14:39:44
Titanium blind flanges are crucial components in various industrial applications, known for their exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. These specialized flanges play a vital role in sealing pipe ends, pressure vessels, and other equipment in demanding environments. Understanding the different sizes and specifications of titanium blind flanges is essential for engineers, designers, and procurement professionals to ensure optimal performance and compatibility in their projects.
What are the standard sizes available for titanium blind flanges?
Titanium blind flanges are manufactured in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various piping systems and applications. The standard sizes typically follow industry norms and can range from small diameters of 1/2 inch (15 mm) up to large diameters of 24 inches (600 mm) or more. Some common sizes include:
- 1/2 inch (15 mm)
- 3/4 inch (20 mm)
- 1 inch (25 mm)
- 1 1/2 inches (40 mm)
- 2 inches (50 mm)
- 3 inches (80 mm)
- 4 inches (100 mm)
- 6 inches (150 mm)
- 8 inches (200 mm)
- 10 inches (250 mm)
- 12 inches (300 mm)
- 16 inches (400 mm)
- 20 inches (500 mm)
- 24 inches (600 mm)
It's important to note that custom sizes can also be manufactured to meet specific project requirements. The size selection depends on factors such as the pipe diameter, system pressure, and flow requirements.
In addition to diameter, titanium blind flanges are also specified by their thickness, which varies depending on the pressure rating and application. Thicker flanges are typically used for higher pressure applications, while thinner flanges may be suitable for lower pressure systems.
When selecting a titanium blind flange, it's crucial to consider not only the nominal pipe size but also the flange class, which determines the pressure-temperature rating of the flange. Common flange classes include 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, and 2500#. Higher class numbers indicate higher pressure ratings.
The bolt hole pattern is another important specification to consider. The number and size of bolt holes must match the mating flange to ensure proper sealing and structural integrity. Standard bolt hole patterns are defined by industry standards such as ASME B16.5 for pipe flanges.
How do titanium blind flange specifications differ from other materials?
Titanium blind flanges offer unique specifications that set them apart from flanges made of other materials such as steel, stainless steel, or alloy metals. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right flange material for a given application.
1. Corrosion Resistance:
One of the most significant advantages of titanium blind flanges is their superior corrosion resistance. Titanium forms a stable, protective oxide layer when exposed to air or moisture, making it highly resistant to various corrosive environments. This property allows titanium flanges to outperform even stainless steel in aggressive media such as seawater, chlorides, and oxidizing acids.
In comparison, carbon steel flanges are prone to rusting and require protective coatings or regular maintenance. Stainless steel offers good corrosion resistance but can still be susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion in certain environments. Titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance translates to longer service life, reduced maintenance costs, and improved safety in critical applications.
2. Strength-to-Weight Ratio:
Titanium blind flanges boast an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, offering high strength comparable to steel while being approximately 45% lighter. This characteristic makes titanium flanges particularly advantageous in applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace, offshore platforms, and mobile equipment.
For instance, a 6-inch (150 mm) titanium blind flange might weigh significantly less than its steel counterpart while maintaining similar or superior mechanical properties. This weight reduction can lead to easier handling, reduced transportation costs, and lower overall structural loads in large-scale projects.
3. Temperature Resistance:
Titanium blind flanges exhibit excellent performance across a wide temperature range. They maintain their mechanical properties from cryogenic temperatures (as low as -320°F or -196°C) up to moderate elevated temperatures (around 600°F or 315°C for most titanium alloys). This temperature versatility makes titanium flanges suitable for diverse applications, from liquefied natural gas (LNG) processing to chemical reactors.
In contrast, carbon steel flanges may become brittle at very low temperatures, while some stainless steel grades can lose strength at elevated temperatures. The consistent performance of titanium across a broad temperature spectrum simplifies design considerations and enhances reliability in variable operating conditions.
4. Chemical Compatibility:
Titanium blind flanges demonstrate exceptional resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including chlorides, sulfuric acid, and organic compounds. This broad chemical compatibility makes them ideal for use in chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and pulp and paper industries.
While stainless steel flanges offer good chemical resistance, they can still be vulnerable to stress corrosion cracking in chloride-rich environments. Carbon steel flanges have limited chemical compatibility and often require special linings or coatings for use in aggressive media. Titanium's natural resistance to various chemicals eliminates the need for additional protective measures in many applications.
5. Biocompatibility:
Titanium blind flanges are highly biocompatible, making them suitable for use in medical and food processing applications. The material's inertness and resistance to bodily fluids have led to its widespread use in medical implants and surgical instruments. In food and beverage processing, titanium flanges can help maintain product purity without the risk of contamination.
This biocompatibility is a unique advantage over many other flange materials. While some grades of stainless steel are also considered biocompatible, titanium's superior properties often make it the preferred choice in critical medical and food-grade applications.
What are the key applications and benefits of using titanium blind flanges?
Titanium blind flanges find extensive use across various industries due to their unique combination of properties. Understanding the key applications and benefits of these specialized components can help engineers and project managers make informed decisions about their use in different scenarios.
1. Offshore and Marine Applications:
One of the primary applications of titanium blind flanges is in offshore oil and gas production and marine environments. The exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium makes it ideal for seawater exposure, where traditional materials like steel or even stainless steel may fail prematurely. Titanium blind flanges are commonly used in:
- Subsea pipelines and manifolds
- Desalination plants
- Offshore platforms and rigs
- Marine heat exchangers
The benefits in these applications include extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved safety. For instance, a titanium blind flange used in a subsea pipeline can withstand the corrosive effects of seawater for decades without significant degradation, minimizing the need for costly underwater repairs or replacements.
2. Chemical Processing Industry:
The chemical industry heavily relies on titanium blind flanges for handling corrosive chemicals and maintaining process integrity. Key applications include:
- Chemical reactors and pressure vessels
- Acid processing equipment
- Chlor-alkali production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
The benefits of using titanium in these environments are numerous. Its resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including chlorides and oxidizing acids, ensures long-term reliability and prevents contamination of process fluids. The material's ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it suitable for demanding chemical reactions, reducing the risk of leaks or failures that could lead to safety hazards or production downtime.
3. Aerospace and Defense:
The aerospace and defense sectors leverage the high strength-to-weight ratio of titanium blind flanges in various applications:
- Aircraft hydraulic systems
- Fuel systems
- Rocket propulsion components
- Military vehicle armor
The primary benefit in these applications is weight reduction without compromising strength or durability. For example, using titanium blind flanges in aircraft fuel systems can contribute to overall weight savings, improving fuel efficiency and increasing payload capacity. The material's fatigue resistance also ensures long-term reliability under the cyclic loading conditions typical in aerospace applications.
4. Power Generation:
Titanium blind flanges play a crucial role in power generation facilities, particularly in environments where corrosion resistance and heat transfer efficiency are paramount:
- Steam turbine systems
- Geothermal power plants
- Nuclear power plant components
- Heat exchangers in power stations
The benefits in power generation applications include improved efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. For instance, titanium blind flanges used in geothermal power plants can withstand the corrosive geothermal fluids and high temperatures, ensuring long-term reliability and minimizing downtime for repairs or replacements.
5. Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Industries:
The biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of titanium make its blind flanges valuable in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications:
- Bioreactors and fermentation vessels
- Sterile processing equipment
- Medical implant manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical storage and transport systems
The key benefit in these industries is the material's ability to maintain product purity and prevent contamination. Titanium's inertness ensures that it doesn't react with sensitive biological or pharmaceutical compounds, making it ideal for applications where product integrity is critical.
6. Pulp and Paper Industry:
The pulp and paper industry utilizes titanium blind flanges in various processes involving corrosive chemicals:
- Bleaching equipment
- Chemical recovery systems
- Paper machine components
- Digester vessels
The benefits in this sector include improved equipment longevity and reduced downtime. Titanium's resistance to chlorine-based bleaching agents and other corrosive chemicals used in paper production ensures that flanges and other components can withstand the harsh operating environment, leading to more reliable and efficient production processes.
7. Desalination Plants:
Titanium blind flanges are extensively used in desalination facilities due to their exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion:
- Reverse osmosis systems
- Multi-stage flash distillation units
- Seawater intake systems
- Brine disposal equipment
The primary benefit in desalination applications is the long-term reliability and reduced maintenance requirements. Titanium components can withstand continuous exposure to seawater and brine solutions without significant corrosion, ensuring the longevity of critical equipment and reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs.
In conclusion, titanium blind flanges offer a unique combination of properties that make them invaluable in a wide range of industrial applications. Their corrosion resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and biocompatibility provide significant benefits in terms of long-term reliability, reduced maintenance costs, and improved safety. While the initial cost of titanium components may be higher than traditional materials, the long-term advantages often result in a lower total cost of ownership, particularly in demanding environments where performance and durability are critical.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance and seek more sustainable solutions, the role of titanium blind flanges is likely to expand. Ongoing research and development in titanium alloys and manufacturing processes may further enhance the properties and cost-effectiveness of these components, opening up new applications and opportunities across various sectors.
At SHAANXI CXMET TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD, we take pride in our extensive product range, which caters to diverse customer needs. Our company is equipped with outstanding production and processing capabilities, ensuring the high quality and precision of our products. We are committed to innovation and continuously strive to develop new products, keeping us at the forefront of our industry. With leading technological development capabilities, we are able to adapt and evolve in a rapidly changing market. Furthermore, we offer customized solutions to meet the specific requirements of our clients. If you are interested in our products or wish to learn more about the intricate details of our offerings, please do not hesitate to contact us at sales@cxmet.com. Our team is always ready to assist you.
References:
1. ASTM International. (2021). "Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Forgings." ASTM B381-21.
2. Titanium Engineers. (2022). "Titanium Flanges: Properties and Applications."
3. Korb, L.J. (2018). "Corrosion in the Petrochemical Industry." ASM International.
4. Donachie, M.J. (2000). "Titanium: A Technical Guide." ASM International.
5. Lütjering, G., & Williams, J.C. (2007). "Titanium." Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
6. Peters, M., Kumpfert, J., Ward, C.H., & Leyens, C. (2003). "Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications." Advanced Engineering Materials, 5(6), 419-427.
7. Schutz, R.W. (2005). "Corrosion of Titanium and Titanium Alloys." ASM Handbook, Volume 13B: Corrosion: Materials, 252-299.
8. Titanium Industries. (2023). "Titanium Flanges: Specifications and Applications."
9. NACE International. (2019). "Corrosion Control in the Refining Industry." NACE International.
10. American Petroleum Institute. (2020). "Specification for Piping Flanges and Fittings." API Specification 6A.